#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Input an integer\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n & 1 == 1)
printf("Odd\n");
else
printf("Even\n");
return 0;
}
Another Way:
//আমি আরেকটু শর্টকাট করি নিচের মত করে
if(num & 1)
printf("odd");
else
printf("even);
Another Way Less Efficient Code:
if ((n & -n) == 1)
printf("odd");
else
printf("even");
Another Way: Using XOR
if ( (num ^ 1) < num)
printf("odd");
else
printf("even");
3. Using Bitwise AND Operator (&)
Bitwise operators work on individual bits of a variable. For example, when you perform an operation on 5 and 1 (5 & 1), the result is 1. Let's see how it works:
5 - 0101 ( 5 in binary form ) - 5 is odd number here.
1 - 0001 ( 1 in binary form )
5 & 1 - 0001 ( result after performing bitwise & i.e 1)
If you see above, after performing bitwise & on 5 and 1, we got result 1. Let's perform bitwise & on 4 (even number ) and 1.
4 - 0100 ( 4 in binary form) - 4 is even number here.
1 - 0001 ( 1 in binary form) - 1 is even number here.
4 & 1 - 0000 ( result is 0)
The rules of Bitwise & when performed on bits 0 and 1.
0 & 0 - 0
0 & 1 - 0
1 & 0 - 0
1 & 1 - 1
Now, let's go through the solution, if you see in the above examples when you perform bitwise & on an odd number and 1, we got result 1, when you perform on even number and 1, it is 0, which means:
( odd number ) & 1 is 1.
( even number ) & 1 is 0.
So the algorithm is:
if( number & 1 == 0) {
even number
} else {
odd number
}
The code snippet is below:
private void isEvenM3(int i) {
int res = i & 1;
if(res == 0) {
System.out.println(i +" is Even Number");
} else {
System.out.println(i + " is Not Even Number");
}
}
4. Using Left Shift and Right Shift Operators (<< , >>)
Similar to Bitwise operators, Left shift and Right shift operators work on individual bits of a number. Let's see how Left shift operator and right shift operator work. For example:
5 >> 1 - (0101) >> 1 = 0010, i.e., 2
Here we performed right shift once, i.e., 5 in binary form is 0101 and doing right shift once, it becomes 0010, as right most digit goes away. Therefore 5 >> 1 is 2. Now let's see how left shift operator works:
5 << 1 - ( 0101 ) << 1 = 1010 i.e.,10
Here, when you do left shift of 1 bit, the left most bit goes away.
Let's see one more example, now take 4 for our purpose.
4 >> 1 - ( 0100 ) >> 1 = 2.
4 << 1 - ( 0100 ) << 1 = 8.
Now we understand how left shift and right shift operators works. Now let's see how to solve our problem using left and right shift operators. Now take 4, 5 for our reference.
Now I am going to perform one right shift and one left shift on both 4 and 5.
( 4 >> 1 ) << 1 = ( 2 ) << 1 = 4.
( 5 >> 1 ) << 1 = ( 2 ) << 1 = 4.
If you observe above, for even numbers, we are getting the same number again, but for odd numbers, we are getting a different number. We can make use of this algorithm to solve our problem.
if ( ( num >> 1) << 1 == num) {
even number
} else {
odd number
}
The code snippet is below:
private void isEvenM4(int i) {
int res = (i >> 1) << 1;
if(res == i) {
System.out.println(i +" is Even Number");
} else {
System.out.println(i + " is Not Even Number");
}
}
Example 2: Check Whether Number is Even or Odd using ternary operators
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> n;
(n % 2 == 0) ? cout << n << " is even." : cout << n << " is odd.";
return 0;
}

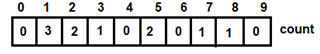 Figure 1: count array
Figure 1: count array Figure 2: Formula for updating count array
Figure 2: Formula for updating count array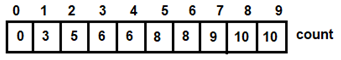 Figure 3 : Updated count array
Figure 3 : Updated count array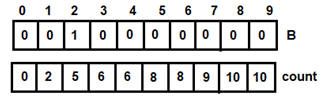 Figure 4: For i=0
Figure 4: For i=0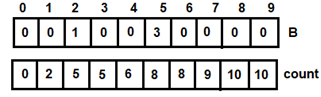 Figure 5: For i=1
Figure 5: For i=1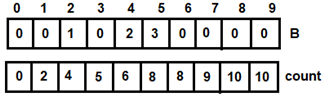 Figure 6: For i=2
Figure 6: For i=2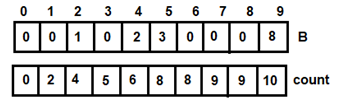 Figure 7: For i=3
Figure 7: For i=3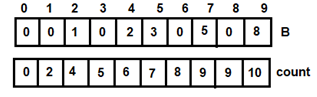 Figure 8: For i=4
Figure 8: For i=4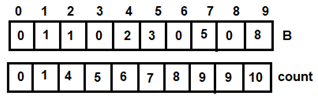 Figure 9: For i=5
Figure 9: For i=5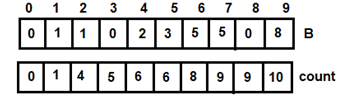 Figure 10: For i=6
Figure 10: For i=6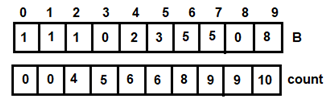 Figure 11: For i=7
Figure 11: For i=7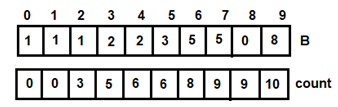 Figure 12: For i=8
Figure 12: For i=8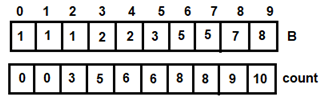 Figure 13: For i=9
Figure 13: For i=9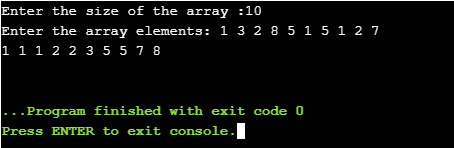 Figure 14: Output of Program
Figure 14: Output of Program